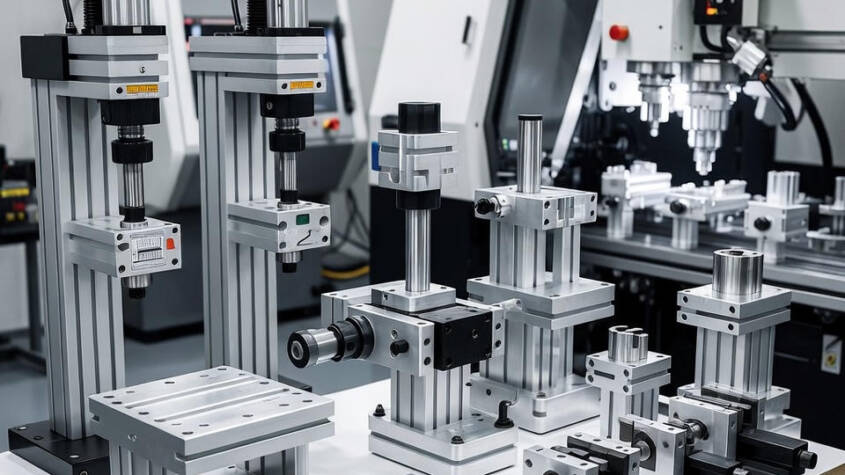
In the CNC manufacturing industry, precision is achieved through a combination of advanced machinery, skilled engineering, and reliable process control systems. While CNC machines execute programmed operations with speed and consistency, the true foundation of machining accuracy lies in how the workpiece is positioned, supported, and stabilized during production. This is why jig and fixture design plays a decisive role in achieving repeatable accuracy, minimizing production errors, and ensuring that every machined component meets strict dimensional requirements from the first part to the last.
As product geometries become more complex and tolerances more demanding, manufacturers can no longer rely on generic tooling solutions. Custom-engineered tooling systems provide the stability and control required to maintain machining integrity under real-world cutting conditions. In high-performance CNC environments, tooling is not an accessory but a critical enabler of efficiency, quality, and scalability.
The Functional Importance of Workholding Tools in CNC Machining Processes
Workholding tools are responsible for securing components firmly in place while machining forces are applied at high speeds and varying directions. Their primary purpose is to prevent movement, distortion, or vibration that could compromise part accuracy. In CNC operations, where automation reduces manual intervention, reliable workholding ensures that each machining cycle produces consistent results without operator-dependent variation. Beyond basic clamping, effective workholding strategies improve productivity by reducing setup time and simplifying changeovers. When parts are located and secured consistently, operators spend less time aligning components and more time producing quality output. This consistency also enhances process reliability, making it easier to identify and correct issues before they escalate into costly production errors.
CNC Fixture Design as the Backbone of Repeatable Accuracy
CNC fixture design focuses on controlling the precise location and orientation of a workpiece relative to machine coordinates. A well-designed fixture establishes stable datums, distributes clamping forces evenly, and provides unobstructed access for cutting tools. These characteristics are essential for maintaining dimensional accuracy throughout multi-step machining operations. In advanced CNC environments, fixtures are often engineered to support multiple operations within a single setup, reducing the need for repositioning. This approach minimizes cumulative errors and improves overall process efficiency. By investing in carefully engineered fixture solutions, manufacturers can achieve higher repeatability, tighter tolerances, and improved confidence in meeting customer specifications.
Machining Support Tooling and Its Role in Process Stability
Machining support tooling provides additional reinforcement for components that are susceptible to deflection or vibration during cutting. Thin-walled parts, complex geometries, and high-value materials all benefit from supplementary support that maintains structural integrity throughout machining cycles. Without proper support, cutting forces can cause dimensional deviations or surface finish defects that are difficult to correct. Stable machining conditions also contribute to longer tool life by reducing chatter and uneven load distribution on cutting edges. When machining support systems are integrated effectively, manufacturers can increase feed rates and reduce cycle times while maintaining quality standards. This balance between speed and precision is a key driver of competitiveness in CNC manufacturing.
Precision Locating Devices for Consistent Dimensional Control
Precision locating devices are essential for establishing accurate reference points during machining. These devices ensure that parts are positioned consistently relative to machine axes, enabling repeatable results across different batches and production runs. Accurate locating is particularly important in multi-axis CNC machining, where even minor misalignment can lead to significant dimensional errors. By incorporating precision locating mechanisms into tooling systems, manufacturers can reduce setup variability and improve overall process control. These devices also support modular tooling concepts, allowing fixtures to be adapted for different components without sacrificing accuracy. As production demands shift toward customization and flexibility, precision locating solutions become increasingly valuable.
Engineering Principles That Define High-Performance Tooling Systems
The effectiveness of any tooling system is determined by its underlying design principles. Material selection, structural rigidity, clamping strategy, and ease of use all influence how well a tooling solution performs over time. Engineers must consider not only immediate machining requirements but also long-term durability and maintenance needs. Thermal behavior is another critical factor in CNC tooling design. Heat generated during machining can cause expansion that affects dimensional accuracy if not properly managed. Tooling systems designed with thermal stability in mind help maintain consistent results even under demanding operating conditions. These considerations ensure that tooling remains reliable throughout extended production cycles.
Digital Design and Simulation in Modern Tooling Development
The use of digital tools has transformed how tooling solutions are designed and validated. CAD and CAM systems allow engineers to simulate machining operations, analyze clamping forces, and identify potential interference before production begins. This digital-first approach reduces development time and minimizes costly design revisions. Simulation-driven tooling development also supports optimization by enabling engineers to test multiple design concepts virtually. By refining tooling solutions in a digital environment, manufacturers can achieve better performance and reliability once the tooling is deployed on the shop floor. This integration of digital engineering enhances both efficiency and quality in CNC manufacturing.
Industry Sectors That Rely on Precision Tooling Solutions
Precision tooling systems are indispensable across industries that demand high accuracy and repeatability. Aerospace manufacturers depend on advanced tooling to machine structural components and engine parts with exacting tolerances. Automotive production environments use precision tooling to support high-volume manufacturing while maintaining consistent quality standards. Medical device manufacturing also relies heavily on precision tooling, where regulatory compliance and dimensional accuracy are critical. Across these industries, the performance of CNC machining operations is closely tied to the quality and reliability of the tooling systems that support them.
Key Advantages Delivered by Advanced CNC Tooling Systems
-
Enhanced dimensional accuracy through stable and repeatable part positioning
-
Reduced setup time and improved changeover efficiency
-
Extended cutting tool life due to minimized vibration and chatter
-
Lower scrap rates and improved overall production consistency
Common Manufacturing Challenges Addressed by Precision Tooling
-
Managing complex geometries and delicate components
-
Maintaining accuracy across multi-axis machining operations
-
Reducing operator-dependent variability in setups
-
Supporting scalable production without compromising quality
The Expanding Role of Tooling in Smart CNC Manufacturing
As CNC manufacturing evolves toward automation and data-driven production, tooling systems are adapting to support smarter processes. Modular designs, quick-change mechanisms, and sensor-enabled fixtures are increasingly used to enhance flexibility and monitoring capabilities. These innovations allow manufacturers to respond quickly to changing production requirements while maintaining precision. In smart manufacturing environments, tooling is becoming an active contributor to process intelligence. By integrating tooling data with machine monitoring systems, manufacturers can gain deeper insights into machining conditions, improve predictive maintenance, and optimize overall performance.
Conclusion: Establishing Long-Term Precision Through Intelligent Tooling
A strong foundation in tooling engineering is essential for manufacturers seeking sustainable success in CNC machining. The fundamental concepts behind jigs and fixtures, including their functions and classifications, are widely documented in technical resources such as Wikipedia’s explanation of jigs and fixtures, which provides valuable context on their role within manufacturing systems.
As CNC technology continues to advance, ongoing research and engineering studies offer deeper insights into tooling innovation and machining accuracy. Additional perspectives on precision manufacturing and tooling optimization can be explored through academic and technical publications accessible via Google, supporting informed decision-making and continuous improvement in CNC production environments.
Freight Forwarding Services in Canada: How Progressive Cargo Simplifies Global Logistics
Freight forwarding plays a crucial role in today’s interconnected global economy. Business…